David Palmer is the Blockchain Lead and IoT at Vodafone Business, In this podcast we discuss the convergence of blockchain, 5G, AI and IoT (Internet of Things). In addition, we discussed the evolution of internet of things to internet of value and some of the exciting work Vodafone is doing in this space from Smart Cities, to supply chain and to the Energy Web Foundation.
David has been working in the telco sector for the last 20 years. He has worked on broadband, ADSL rollout, satellite broadband and for the last 10 years on IoT including combining it with blockchain for the last 4 years.
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a distributed ledger that is shared between different parties. When you combine that with transactions you get to the basis of the first use case of blockchain which is Bitcoin. Bitcoin demonstrated how you can build trust by having transactions written on a shared and distributed ledger where different parties validate the transactions and provide its security through their combined computational power.
David notes that this is a simple definition of blockchain. Over the last three years there has been an evolution of blockchain. On one end you have public blockchains such as Bitcoin, Ethereum versus private blockchains with permissioned access formed by consortiums. Issues of interoperability arise when you try to bring those different blockchains together. In addition there are different protocols and consensus mechanisms that come in to play from DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph), proof of stake and proof of work.
Blockchain is a continuously evolving technology, but at its core it is a technology about trust. David mentions that there is a lot of friction today in everyday process. These are essentially processes built to establishing trust. The real power of blockchain is in providing a trusted shared platform to automate those process to remove that friction. Blockchain’s role in digital transformation is in the removal of the trust issue, it’s in the automation of processes which will give rise to a new evolution of automated business models and processes.
Explosion in IoT devices
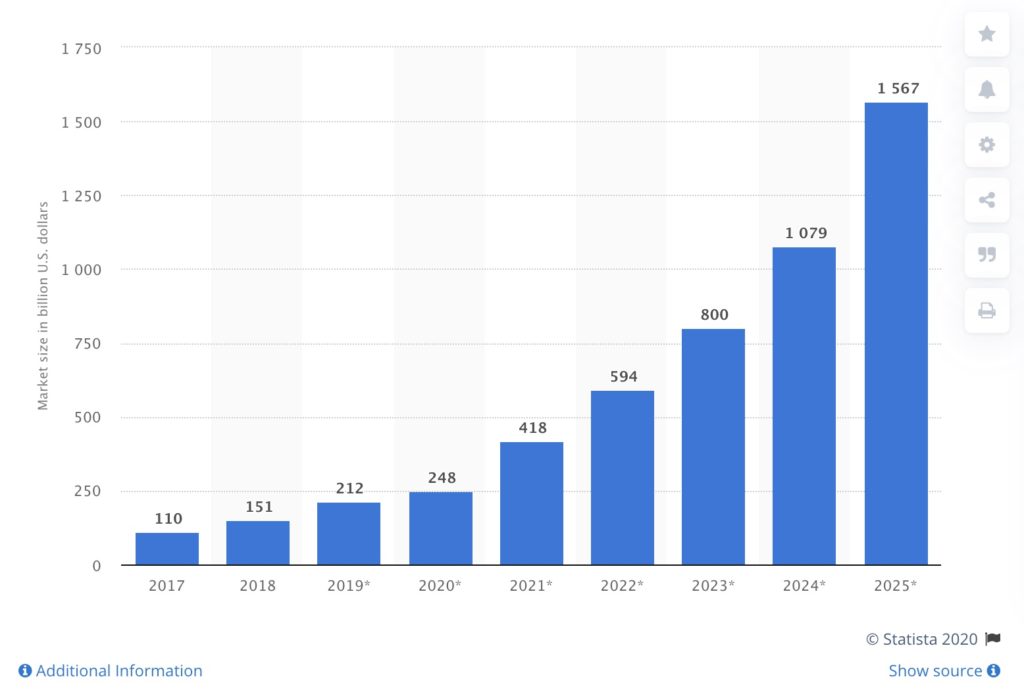
Statista is forecasting end-user spending on IoT solutions to reach $1.6 trillion by 2025 from 21.5 billion IoT devices. These are staggering numbers! With the increase adoption of 5G these IoT devices will be able to provide large amounts of data within nano-seconds.
Vodafone has a Global IoT platform called Global Digital Services Platform (GDSP). This platform is at the very heart of the IoT offering to Vodafone’s customers, and is also offered as an IoT platform to other Telco’s. The GDSP provides all the management facilities for customers and channels to manage their individual IoT SIM estates.
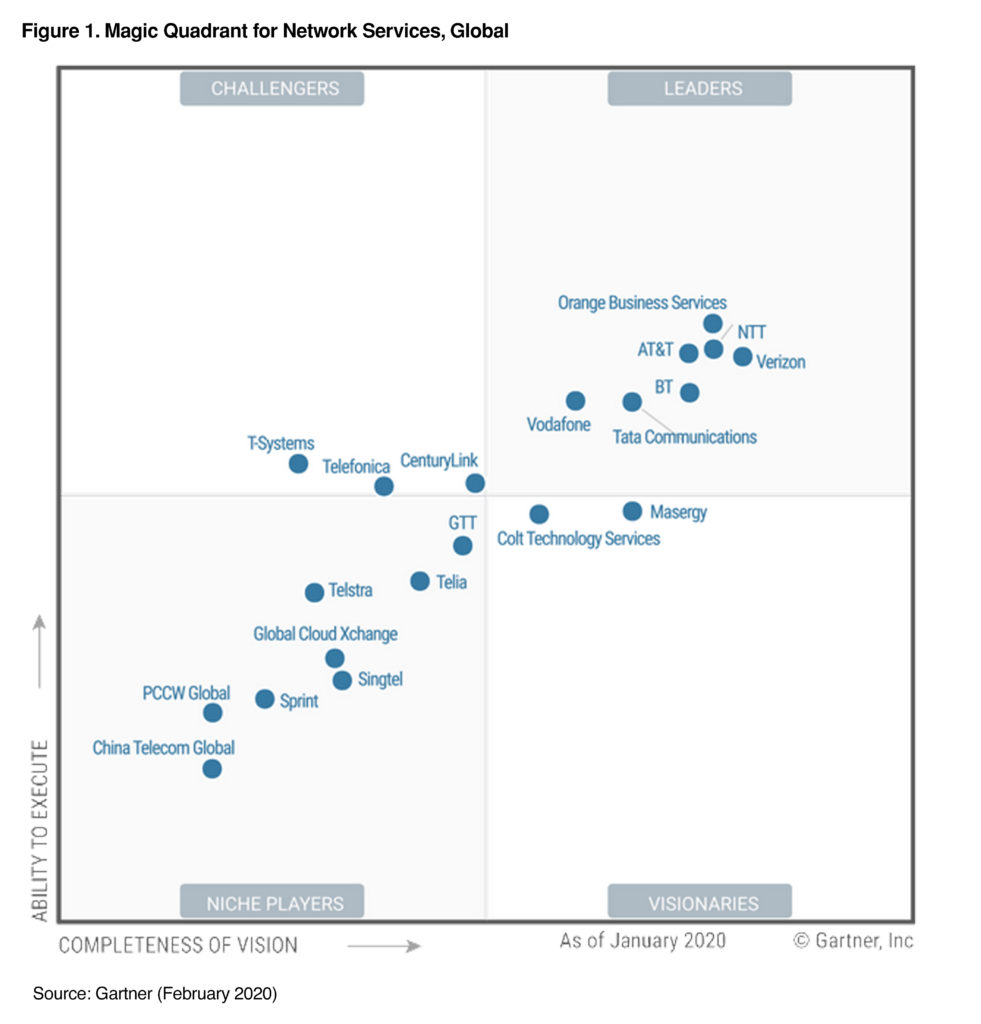
Vodafone has been a leader in IoT for the last 10 years as recognised by Gartner’s Magic Quadrant.
What IoT allows businesses to do is to digitise their assets. It allows for those assets to produce data which unlocks new business models and monetisation opportunities. This is a space that Vodafone has experience in which it has been putting to use in helping its clients.
David has seen supply chain as a key industry that is seeing a large growth in IoT devices. For example with recent conversations of the Pfizer vaccine that has to be kept at minus 70 degrees, how is that ensured? You need data from devices at the manufacturer, to supply chain, to delivery which can be provided by IoT devices.
Getting the trust in the data and provenance of the information will need some form of distributed architecture and distributed solution, so that the parties in that can have trust in the data that’s been produced.
Pfizer and the vaccine distribution is a prime example of where new emerging technologies such as IoT, AIs to help manage the risk and blockchain can come together to make a real difference.
Transition of Internet of Things to Internet of Value
Raghavendra Kulkarni, from Bosch, was on Insureblocks to discuss Bosch’s Economy of Things, where he explained the movement of IoT devices to EoT (Economy of Things). David believes that Bosch has a similar vision to them where Economy of Things is basically taking IoT from Level 1 to Level 2. Level 1 is the billions of IoT devices producing data, where those data are siloed within the organisation that is producing them. The next layer, Level 2, is where those billions of devices are interacting and transacting with each other to execute on business use cases.
Smartphones have revolutionised business models. Most people don’t use their smart phone to make phone calls or send texts but to use them for their applications. The phone becomes the starting point or the customer edge point for doing multiple things. That has been a revolution that has been happening from 2007 to now. The next big revolution is in getting a thing such as a car or any other device that a business or a person who owns to automatically interact and transact with each other. That is the foundation of the economy of things. Blockchain will play an important role in that next revolution by establishing trust. It will establish the trust between people, business and devices to allow new transactions and new business models between them.
Convergence of 5G, AI and blockchain
5G offers low latency technology which means you can start to process data more quickly than before. This enables numerous new solutions such as autonomous level 4 for vehicles and opens up new business models.
When looking at data marketplaces, 5G, AI and blockchain each play a key component. 5G provides the speed and low latency that gives rise to new business models.
AI finds data that is useful and monetizable. For example, in automated transactions data can be used to find opportunities to either fill spare capacity or improve utilisation of connected resource.
Blockchain, being the trust anchor, pulls all of those things together.
Convergence of public with private blockchains
Permission blockchain gives enterprises, the opportunity to dip their toes into blockchain to see some value within a controlled environment. Permissioned blockchains offers enterprises both security and control which has led to some successful implementation such as IBM’s TradeLens (TradeLens on Insureblocks).
David believes that what we’re seeing now with technology is the trend for barriers to entry to come down. He gives the example of the taxi industry which previously had large barriers of entry in terms of licenses and then you have Uber & Lyft who come a long with an over the top solution based on technology which disrupted that industry.
When the barrier of entry comes down then you need to expand the trust because you’ve got new participants who are entering it. Those market forces will lead to convergence of permissioned blockchains. You will potentially have one out of two models which will emerge:
- Interoperable two layers of permissioned and public blockchain that is more consolidated and refined than now
- Or as the internet you will have a convergence towards public blockchain
Vodafone and Smart Cities
Smart cities are the first use cases where you can join up things that are connect that are producing data. You can exploit that to establish a sharing economy and new business models. For that to happen you need three things:
- Devices that produce data to be connected
- Algorithms that turn that data into information intelligence
- Trust powered by blockchain
Autonomous vehicles and mobility is a key component for smart cities. Vodafone has had a number of interactions with MOBIfor autonomous vehicles. These were more technical proof points where a car could automatically transact for parking or tolling.
Blockchain based digital identity partnered with smart contracts, which can dictate the terms between two actors, is the basis for autonomous transactions for autonomous vehicles, for example, to park and pay their toll.
Role of SIM cards
SIM Cards are an important part of the connectivity cycle. SIM cards aren’t just for handsets, for example, Vodafone’s IoT platform has a roaming global SIM card in it. SIM cards play the role of an important edge point with the link to blockchains, to transactions and to identities. The encryption technologies that telcos have is both proven and scalable which is an area blockchain platforms have traditionally struggled with.
Decentralised digital identity is a cornerstone technology that enables the connection of things to blockchain to establish trust. One approach for providing that digital identity is the one provided by SIM cards. There are other elements of digital identity such as DIDs.
Decentralized identifiers (DIDs) are a new type of identifier that enables verifiable, decentralized digital identity. A DID identifies any subject (e.g., a person, organization, thing, data model, abstract entity, etc.) that the controller of the DID decides that it identifies.
What this means is that one’s car can be part of their identity. That car can then participate for its owner in some form of transaction.
Energy Web Foundation
In late 2019 Vodafone formed a partnership with the Energy Web Foundation to integrate distributed energy resources (DERs) with power grids using IoT and blockchain technology.
The Energy Web Foundation has two main goals: (1) to bring transparency to auditing carbon footprint and how energy is produced. (2) to extend the grid beyond the traditional grid by allowing the use of solar panels and storage solutions from car batters as part of a flexi grid.
All of these energy assets including solar panels, wind turbines need to communicate with the grid in a secure a manner and will need identity to do this. Vodafone can deploy SIM centric blockchain identity with IoT connectivity. This will enable not just communication and identity but also facilitate transaction between the different assets.