Mance Harmon, CEO of Hedera Hashgraph has returned to Insureblocks to discuss the exciting news of Google joining the Hedera Hashgraph Governing Council. We also discussed the addition of Hedera’s new service entitled, Hedera Consensus Service, which brings interesting opportunities for enterprise blockchain platforms such as Hyperledger and Corda to embrace the opportunity to create verifiable timestamps and ordering of events to a public level trust.
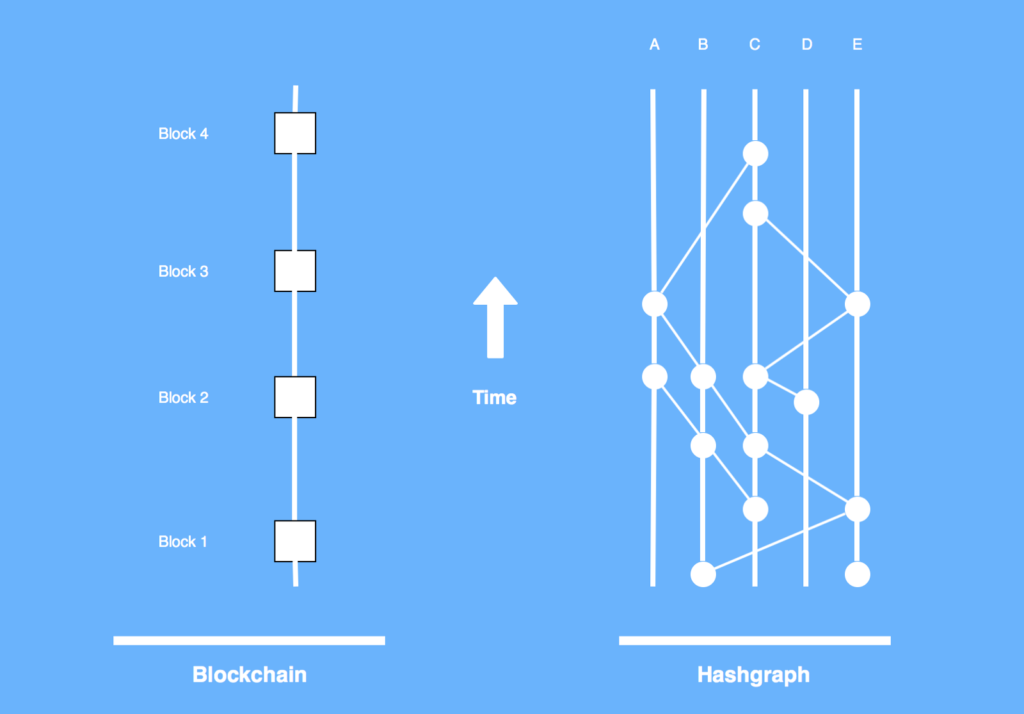
What is blockchain and what is hashgraph?
Blockchain as a term refers to two things:
- A data structure which is a chain of blocks of transactions
- A consensus algorithm that enables a community of participants, each of which holds a local copy of that chain of blocks to come to an agreement or consensus on which block to put next on the top of that chain in order for everyone to keep a consistent chain of blocks
Unfortunately such a blockchain is designed to be slow for a number of reasons:
- Proof of work, the use of a really hard cryptographic puzzle, to reach consensus is time consuming
- From an architectural standpoint, having a single chain that everyone uses is also limiting
Hashgraph, similarly is a term that refers to both a data structure and a consensus algorithm. Hashgraph’s data structure is a graph, in a mathematical sense, whose nodes or vertices are linked together with hashes cryptographically.
Its consensus algorithm makes it possible for those that have a copy of the hashgraph to calculate how the other nodes in the network would vote in order to come to an agreement on the order of transactions.
Because it’s a graph rather than a chain, all of the transactions are flowing into the network, can be processed simultaneously without the need for proof of work.
Hashgraph thus removes the two constraining factors of blockchain: no need for proof of work and a graph instead of a single chain. The result is much higher performance and higher level of security due hashgraph using asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance.
What is Hedera Hashgraph?
Google joins Hedera’s Governing Council
The Council was designed to provide a governing body that the market would trust in doing a good job in terms of shepherding this global network to full maturity and beyond. The Council makes decisions on a wide range of topics such as product roadmap and in control of treasury management. Council members can serve up to two or three year terms. The Council will ultimately be composed of 39 members to represent the full range of use cases across industries, geographies and through time. The council members are chosen to be the largest and most respected members in their categories and geographies. Today there are 11 members: Swisscom blockchain, Tata communications, Nomura, IBM, Boeing, Google, Magalu, Deutsche Telekom, FIS, DLA Piper, and Swirlds.
On the 11th of February, Google became the 11th member of the Hedera Governing Council.
Hedera is a Delaware based LLC, which is a business vehicle with a legal existence separate and distinct from its owners. Council members are members of the LLC in the legal sense. What this means is that full diligence, M&A and approval by the CEO / Board of that organisation is necessary for them to becoming co-owners of Hedera Hashgraph.
The council functions in a very similar fashion to a standards body and has oversight of the organisation itself by committee. Members sit on committees related to their level of expertise for example a tech steering committee, a legal & regulatory committee and marketing committee amongst others.
How to avoid collusion between council members?
As the council members have a little over two thirds of the Hedera Hashgraph tokens there is only a third of the tokens in the market in circulation. This ensures that the risk of a Sibyl attacks are removed. As you don’t have to worry about a bad actor buying up a third or more of the token supply and being able to disrupt consensus.
The next question is to ensure that the chosen members of the council don’t collude and to do that you select members that are large enough and care far more about their individual brands and lines of businesses for them to risk their reputation on colluding over this public distributed ledger.
Additionally a principle reason for having the council members geographical, industry wide distributed and distributed over time was to avoid collusion between members.
Similarities between Hedera’s Governing Council and the Libra Association?
The press has made numerous comparisons to Google joining the Hedera governing council to Libra’s loss of members from its association. The comparison isn’t fair as Libra is focused on being a payment solution and Hedera isn’t. Libra’s intention of creating a stable coin has brought it into regulatory complexities that Hedera doesn’t have.
Hedera is focused on trying to create the trust layer of the internet in its most general sense. They are taking to market consensus as a service for the full range of use cases for public, private enterprises and small businesses.
Why Google? Why not Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure?
Mance believes that Google took notice of Hedera making use of Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Mance also states that Hedera’s architecture that they’re taking to market, lends itself very well to their strategy to grow GCP. Hedera’s launch of the Hedera Consensus Service also sits well with GCP’s strategy. The consensus service is Hedera’s fourth service in addition to the original three being cryptocurrency, file storage and smart contracts.
Hedera Consensus Service
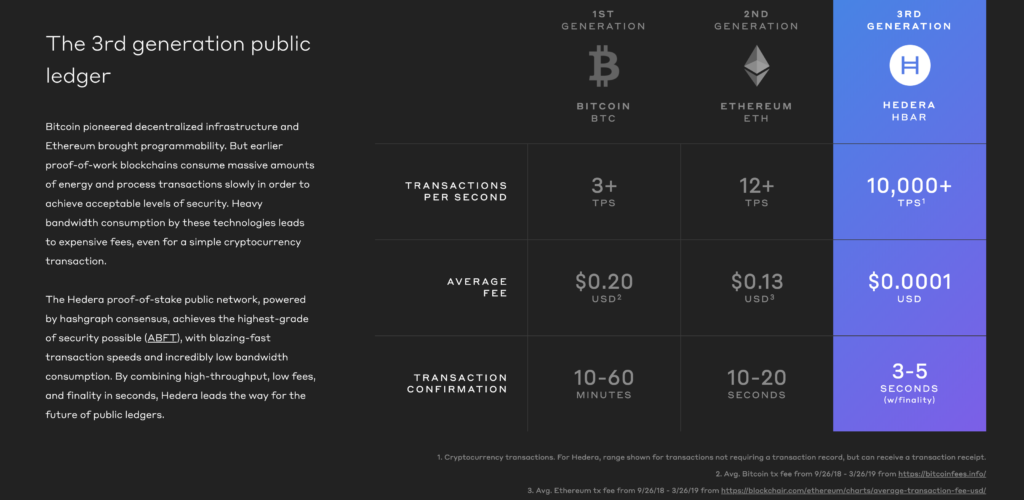
Mance believes that the challenge of public blockchain networks such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and EOS for example, also referred to as the “1st layer of blockchain”, is that they conflate two separate functions:
- As transactions flow into the network they are put into consensus order
- Secondly, these transactions then feed into another layer of business logic, often referred to as smart contracts. The smart contracts validate the transactions for some form of application
The above two functions are very different functions but they exist on the same network. This kind of architectures creates a number of problems:
- Privacy for smart contracts
- Competing CPU resources
Privacy for smart contracts: For smart contracts to operate they need data that is in plain text, not encrypted, for them to know the values within the data in order to calculate an output. In other words, privacy isn’t guaranteed as the data is going to be public.
Competing CPU resources: As smart contracts are executing on a public network that means the developer of the smart contract is competing for CPU resources. If traction is gained that can generate issues of scalability.
With a private network you get privacy and confidentiality however the problem is that, according to Mance, private networks aren’t particularly good with respect to consensus models. In a public network you have hundreds or thousands of nodes putting transactions in order in a distributed manner. On a private network you might have four or six that are operating in a single data centre where those consensus nodes are managed by a single entity. This is as good as a central database.
What Hedera has done is taken the public network model and split those two layers apart. One layer, the transaction ordering is being offered as a service. The second layer, transaction validation is moved into a private network and these are called appnets or application networks.
Enterprises will be able to create applications or have their ledger run on multiple computers in a private network or possibly on Google Cloud platform and the transactions through the Hedera Consensus Service (HCS). HCS will provide a unique opportunity to create verifiable timestamps and ordering of events for the application. This service takes full advantage of Hashgraphs’ high-throughput for speed and asynchronous Byzantine fault tolerance for security.
Examples of how companies might utilize HCS include asset tracking across a supply chain, music stream counts to determine remittance for digital rights management, an auditable log of asset transfers, and payable events across an advertising platform
Mance believes that Google believes in that vision which is why they have joined the Hedera Governing Council.
Hedera enhancing private enterprise blockchain platform like Corda or Hyperledger Fabric
Mance quickly states that Hedera isn’t competing with Corda or Hyperledger Fabric but is complementary to those enterprise blockchain platforms. On the 12th of August 2019, IBM joined the Hedera Governing Council. One of the reasons that they joined the council is because they recognised the opportunity for Hyperledger to take advantage of HCS.
Existing Hyperledger applications can remove the RAFT or Kafka consensus engine with the HCS. This provides the Hyperledger application with the benefits of public level trust and performance that a graph can provide and security. This is equally applicable for Corda. Corda has a notary service which Hedera could replace with HCS which is in a sense a trusted, distributed public notary service.
Growing the Hedera Governing Council
As stated earlier Hedera is looking to grow its council from 11 to 39. Mance state that early on they were focusing on having Global 1000 companies or the equivalent of Fortune 500 across geographical regions. However, he believes there are now opportunities to have a few select universities and NGOs to join the governing council.